Can you tell us a little about your background and experience and what led you to MU libraries?
I made up my mind to become a librarian when I was just a kid after seeing my hometown librarian, Anna Detjen, walk to a shelf, pull off a book, open it to a page, and say: “There’s the answer to your question.” How did she do that? How could I learn to do that? I wanted to be a public librarian – I didn’t even know medical libraries existed – but when I tried to set up an internship in college, none were available in public libraries. I was given the choice between an internship in a patient library in a hospital for the criminally insane or in a nursing school library, so I chose the latter. And once there, I found out about the Medical Subject Heading vocabulary, which is used for organizing medical journal articles and books. It made so much sense. I opted for medical librarianship and never looked back.
I interviewed at MU back in 1980 when I was finishing library school at the University of Minnesota. It was a beautiful spring day, and I fell in love with Columbia and knew right away I wanted to come here.
What are some of the unique aspects of your job?
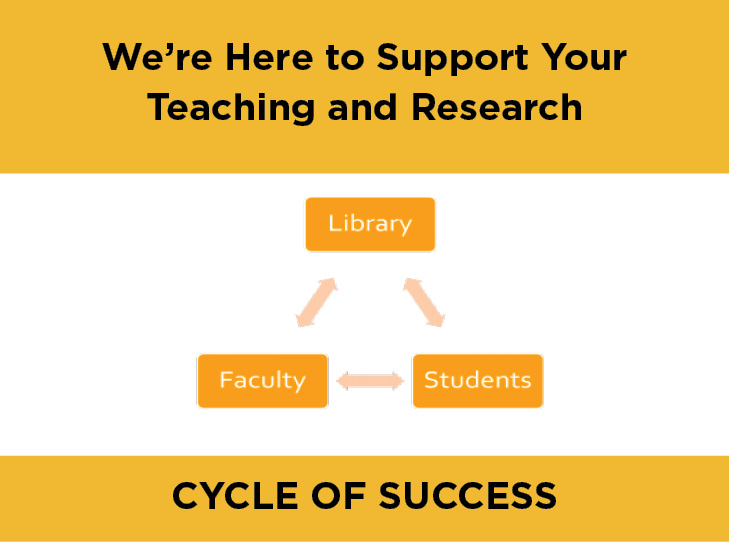
Here in the J. Otto Lottes Health Sciences Library, we spend a lot of time and effort trying to bring our services and collections to our users as part of their normal workflow. Some of us work with clinical teams, answering questions as they arise. In that context, we go beyond simply supplying bibliographies and reference lists to providing summary and synthesis of results.
I’ve also served as co-investigator on systematic reviews, a research method in which you search for, analyze and summarize all of the studies addressing a specific clinical question. I develop the searches and document the search strategies for the research protocol. Librarians are uniquely qualified for this role since it is our business to be familiar with the history, quirks and vagaries of different databases and search engines.
What are some of the ways technology has changed the way your library offers reference services?
Two recent exciting developments, proactive chat and co-browsing, have really helped us amp up our level of service. With proactive chat, if somebody sits on one of our webpages for more than a minute or two, a window pops up to ask them if they need any help. Another recent addition that people really seem to like is co-browsing. When somebody comes into the chat room and needs help doing a search, we can share our screen and talk them through each step in the search. At the conclusion of one recent session, a user told me, "This may have been the most helpful customer service experience in my life."
It’s fun to look back at how far we’ve come. When I started in 1980, our library had two computers, which communicated over phone lines to the National Library of Medicine and the OCLC Library Catalog service. With the latter, we couldn’t just search for a book title, we had to use coded search keys. And we couldn’t search for organization names until after 4 p.m. because it would overwhelm the computer.
Even though the tools have changed dramatically, our core service of helping people get answers to their questions is still much the same.
What types of renovation are needed in the Health Sciences Library in order to better serve your patrons?
It will come as no surprise to anyone who has visited the Health Sciences Library that much of our carpeting and many of our chairs are older than most of our students!
Since the medical and health professions curriculum focuses on small-group learning, we need collaborative spaces where our students can work together in small groups without disturbing those studying around them.
I would like to have white noise machines installed so that people on the third floor can’t hear conversations from two floors below, and vice versa. We’ve had heating and cooling issues in this building ever since it opened, and it’s my fervent hope that we can address these issues in the renovations.
I also think a renovation of the Health Sciences Library would provide an opportunity to retrofit an aging building to make it more energy-efficient. Library buildings much older than ours have achieved LEED gold certification by installing energy-efficient lighting, heating, cooling and plumbing and by choosing furnishings that make use of recycled content.
In this age of mobile computing, we are returning to an era when we can focus on designing spaces to meet the needs of people rather than machines. People will be bringing their increasingly portable computers with them, so we don’t need to have as many computer desks. Instead, we can focus on an inviting mixture of desks for individual study, small-group study areas, and soft seating where people can put their feet up.











 Chris Allman of Charlotte, North Carolina, studies library and information science at the University of North Carolina at Greensboro. He wants to learn more about how the local news startup Charlotte Agenda is preserving its born-digital news content, and develop additional guidelines for how Charlotte Agenda staff can improve those efforts.
Chris Allman of Charlotte, North Carolina, studies library and information science at the University of North Carolina at Greensboro. He wants to learn more about how the local news startup Charlotte Agenda is preserving its born-digital news content, and develop additional guidelines for how Charlotte Agenda staff can improve those efforts.
 John Berlin of Suffolk, Virginia, is a computer science student at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia, where he works for the Web Science and Digital Libraries Research Group. His project goal is to improve the Web Archiving Integration Layer (WAIL) software system by adding a feature to enable users to specify criteria to track news or other content from media platforms such as Twitter. Once identified, this content could then be archived automatically.
John Berlin of Suffolk, Virginia, is a computer science student at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia, where he works for the Web Science and Digital Libraries Research Group. His project goal is to improve the Web Archiving Integration Layer (WAIL) software system by adding a feature to enable users to specify criteria to track news or other content from media platforms such as Twitter. Once identified, this content could then be archived automatically.
 Terry Britt of Sweetwater, Tennessee, is a doctoral candidate studying journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. He will write a research paper on the significance of efforts to assure the lifespan and accessibility of local online news content.
Terry Britt of Sweetwater, Tennessee, is a doctoral candidate studying journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. He will write a research paper on the significance of efforts to assure the lifespan and accessibility of local online news content.
 Itza Carbajal of New Orleans, Louisiana, is an information studies scholar at the University of Texas in Austin. She plans to conduct a research project that lists tools such as ArchiveReady.com that measure the ability for a website to be archived properly. She then plans to assess the web archiving readiness of a variety of online news providers.
Itza Carbajal of New Orleans, Louisiana, is an information studies scholar at the University of Texas in Austin. She plans to conduct a research project that lists tools such as ArchiveReady.com that measure the ability for a website to be archived properly. She then plans to assess the web archiving readiness of a variety of online news providers.
 Jiwon Choi of Osan, South Korea, is studying convergence journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She plans to meet with international students from the University of Missouri to explore how to protect online media content and develop possible solutions.
Jiwon Choi of Osan, South Korea, is studying convergence journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She plans to meet with international students from the University of Missouri to explore how to protect online media content and develop possible solutions.
 Alison Guillory of Belmont, Massachusetts, is a library and information science scholar at Wayne State University in Detroit. She wants to determine which technologies have successfully protected content from the memory hole and which haven’t by studying how news saved in a digital format have fared over a 20-year period. She plans to document what she learns in a timeline.
Alison Guillory of Belmont, Massachusetts, is a library and information science scholar at Wayne State University in Detroit. She wants to determine which technologies have successfully protected content from the memory hole and which haven’t by studying how news saved in a digital format have fared over a 20-year period. She plans to document what she learns in a timeline.
 Matt Hellman of Austin, Texas, is a journalism student at the University of Missouri in Columbia. His project involves a case study of how the Columbia Missourian photography staff is using open source software to provide access to and create a cloud-based long-term archive for digital content.
Matt Hellman of Austin, Texas, is a journalism student at the University of Missouri in Columbia. His project involves a case study of how the Columbia Missourian photography staff is using open source software to provide access to and create a cloud-based long-term archive for digital content.
 Shawn Jones of Virginia Beach, Virginia, is a computer science student at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia. His project will explore the potential relationship between social media sharing of news articles and how quickly those articles are identified by web crawlers as candidates for archiving.
Shawn Jones of Virginia Beach, Virginia, is a computer science student at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia. His project will explore the potential relationship between social media sharing of news articles and how quickly those articles are identified by web crawlers as candidates for archiving.
 Mat Kelly of LaBelle, Florida, is a doctoral candidate studying computer science at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia. His project addresses the need to provide individuals with ways to collect, archive and access news content they perceive as important. Kelly’s work is intended to supplement the large-scale collection work being done by institutions such as the Internet Archive and Library of Congress.
Mat Kelly of LaBelle, Florida, is a doctoral candidate studying computer science at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia. His project addresses the need to provide individuals with ways to collect, archive and access news content they perceive as important. Kelly’s work is intended to supplement the large-scale collection work being done by institutions such as the Internet Archive and Library of Congress.
 Eva Revear of Puyallup, Washington, studies journalism at New York University in New York. Her goal is to find a way to preserve data-driven news applications such as ProPublica’s
Eva Revear of Puyallup, Washington, studies journalism at New York University in New York. Her goal is to find a way to preserve data-driven news applications such as ProPublica’s  Hanna Soltys of St. Louis studies library and information science at Simmons College in Boston. Her project examines questions surrounding how to create more complete preservation methods that accommodate the complexity of digital news platforms. She will also investigate why current archival practices are struggling to preserve online news content.
Hanna Soltys of St. Louis studies library and information science at Simmons College in Boston. Her project examines questions surrounding how to create more complete preservation methods that accommodate the complexity of digital news platforms. She will also investigate why current archival practices are struggling to preserve online news content.
 Carolina Vargas of Fort Lauderdale, Florida, studies journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She wants to reach journalism students with messages that increase awareness of the problem of born-digital content loss and provide options for solving this problem.
Carolina Vargas of Fort Lauderdale, Florida, studies journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She wants to reach journalism students with messages that increase awareness of the problem of born-digital content loss and provide options for solving this problem.
 Tamar Wilner of Dallas studies journalism through the University of Missouri’s online journalism master’s program. She seeks to address problems associated with inaccurate and outdated news content by exploring technology that supports online correction methods.
Tamar Wilner of Dallas studies journalism through the University of Missouri’s online journalism master’s program. She seeks to address problems associated with inaccurate and outdated news content by exploring technology that supports online correction methods.
 Elizabeth Zirk, of Palatine, Illinois, studies journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She will help author and edit a white paper about the forum outcomes. This will include gathering details about the proposed national agenda for preserving born-digital news, projects proposed by working groups and reports summarizing panels and presentations from the event.
Elizabeth Zirk, of Palatine, Illinois, studies journalism at the University of Missouri in Columbia. She will help author and edit a white paper about the forum outcomes. This will include gathering details about the proposed national agenda for preserving born-digital news, projects proposed by working groups and reports summarizing panels and presentations from the event.


