“This daylight-saving plan will afford an opportunity to many thousands of working people, those who work in offices and in factories and in mills and probably in mines, and on railroads, so that if they feel disposed they will have an opportunity to use an hour in the evening, or more, to till their gardens. If we are going to start an individual conservation scheme, and it looks as though that idea is going to take root, it will be one of the blessings that will grow out of this world difficulty. It will get the people back to the land, if it is only a square rod or two. It will give them an opportunity to know how to raise produce.”
Thus spoke Mr. Arthur E. Holder, representing the American Federation of Labor, at a hearing before the Committee on Interstate Commerce on Thursday, May 3, 1917, where he was adding his voice to the support of a bill to establish a daylight saving time in the United States.

The 1958 Interstate Commerce Commission monograph Standard Time by Thomas E. Pyne examines the Standard Time Act, the result of ‘the agitation for ‘daylight saving’ during World War I to conserve fuel and increase national efficiency”, which caused the first national daylight saving to be inaugurated at 2 o’clock on March 31, 1918.
“The act, approved March 19, 1918, is entitled ‘An act to save daylight and to provide standard time for the United States.’ It served a twofold purpose. It divided the territory of the continental United States into five zones, eastern, central, mountain, Pacific, and Alaska…. It also provided that the time of each zone should be advanced 1 hour on the last Sunday in March of each year and returned to normal time on the last Sunday of October…”
The document gives a glimpse of the situation prior to this act, when each State adopted one of four standards of time “for its own use by statute, ordinance, or more usually, public sentiment or habits”:
“The areas embracing the States, cities, towns, and railroads observing the same standard of time were so irregular as to preclude an attempt to define them even approximately. In some instances localities employed a different time form that of the railroad serving them, and in other instances two railroads serving the same point used different standards of time.”
Imagine how difficult that must have made coordinating travel and the transport of goods!
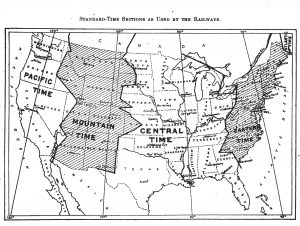
While the daylight saving provision of this Standard Time Act was short lived (it ended after only two summers), other national daylight saving laws have a curious history in the U.S.—one was reinstated year round during World War II, another was passed in 1966, more—that you can learn more about by visiting the Government Information department at Ellis Library after you enjoy an extra hour of sleep on Sunday.
And now you know a bit more about daylight saving time in the United States, how it was initially coupled with the standardization of the time zones and how it was influenced by railroads and the World Wars.
